 |
| What is DHCP and how it work ? |
1-DHCP negotiation (DORA) :
When a DHCP client initiates access to a TCP / IP network, the process of obtaining the IP lease takes place in 4 phases:
1 - The client issues an IP lease request message (DHCPDISCOVER) which is sent as a broadcast over the network with source IP address 0.0.0.0 and destination IP address 255.255.255.255 and MAC address.
2 - The DHCP servers respond by proposing an IP address with a lease time and the IP address of the DHCP server (DHCOFFER)
3 - The client selects the first IP address (if there are several DHCP servers) received and sends a request to use this address to the DHCP server (DHCPREQUEST). His message sent by broadcast includes the identification of the selected server who is informed that his offer has been selected; all other DHCP servers withdraw their offer and the proposed addresses become available again.
4 - The DHCP server acknowledges the request and grants the lease address (DHCPACK), the other servers remove their proposal.
Finally the client uses the address to connect to the network.
1 - The client issues an IP lease request message (DHCPDISCOVER) which is sent as a broadcast over the network with source IP address 0.0.0.0 and destination IP address 255.255.255.255 and MAC address.
2 - The DHCP servers respond by proposing an IP address with a lease time and the IP address of the DHCP server (DHCOFFER)
3 - The client selects the first IP address (if there are several DHCP servers) received and sends a request to use this address to the DHCP server (DHCPREQUEST). His message sent by broadcast includes the identification of the selected server who is informed that his offer has been selected; all other DHCP servers withdraw their offer and the proposed addresses become available again.
4 - The DHCP server acknowledges the request and grants the lease address (DHCPACK), the other servers remove their proposal.
Finally the client uses the address to connect to the network.
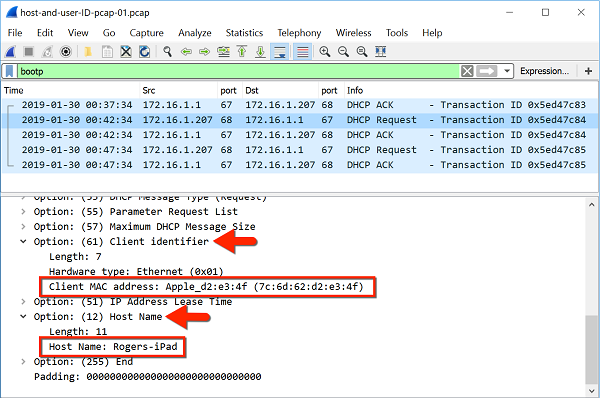
Capture From wireshark :
What is a DHCP lease ?
When a client restarts, it tries to obtain a lease for the same address with the original DHCP server, issuing a DHCPREQUEST. If the attempt is unsuccessful, the client continues to use the same IP address if there is time left on their lease.
DHCP clients on a Windows DHCP server (NT / 2000) attempt to renew their lease when they reach 50% of their duration with a DHCPREQUEST. If the DHCP server is available it sends a DHCPACK with the new duration and possibly the updates of the configuration parameters.
If at 50% the lease could not be renewed, the client tries to contact all the DHCP servers (broadcast) when it reaches 87.5% of its lease, with a DHCPREQUEST, the servers respond either by DHCPACK or DHCPNACK (unusable address, disabled range ...).
When the lease expires or a DHCPNACK message is received the client must stop using the IP address and request a new lease (return to the subscription process). When the lease expires and the client does not get another address, TCP / IP communication stops.
Note: If the request is unsuccessful and the lease has not expired, the client continues to use its IP settings.
DHCP clients on a Windows DHCP server (NT / 2000) attempt to renew their lease when they reach 50% of their duration with a DHCPREQUEST. If the DHCP server is available it sends a DHCPACK with the new duration and possibly the updates of the configuration parameters.
If at 50% the lease could not be renewed, the client tries to contact all the DHCP servers (broadcast) when it reaches 87.5% of its lease, with a DHCPREQUEST, the servers respond either by DHCPACK or DHCPNACK (unusable address, disabled range ...).
When the lease expires or a DHCPNACK message is received the client must stop using the IP address and request a new lease (return to the subscription process). When the lease expires and the client does not get another address, TCP / IP communication stops.
Note: If the request is unsuccessful and the lease has not expired, the client continues to use its IP settings.





0 Comments